This was probably due to binding of the metal to the extramatricial mycelium of the fungus, without affecting the exchange of beneficial substances.[52].  The association is sometimes mutualistic. Hint: Mycorrhiza is the relation between the root of the plant and the fungus with mutual benefits, and they are divided into ecto and endo mycorrhizae types. Brussels sprouts, cabbage/kale, carnation, cauliflower, collards, cranberry, heath, Both soluble and i Ans. The significance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi includes alleviation of salt stress and its beneficial effects on plant growth and productivity. Among symbiotic fungi, those that enter into mycorrhizal relationships and those that enter into relationships with algae to form lichens (see below Form and function of lichens) are probably the best-known. During the winter, when the days are shorter and the amount of light available is decreased, certain plants generate little or no nutrients and must rely on fungus for sugars, nitrogenous compounds, and other nutrients that the fungi may take from waste items in the soil. Milk vine weed is being eradicated from citrus with class 12 biology CBSE, What will be the amount of DNA in a pollen grain if class 12 biology CBSE, Maximum genetic diversity of crop plants occurs where class 12 biology CBSE, Give one means of requiring the ability to detect class 12 biology CBSE, How is fructose a reducing sugar class 12 biology CBSE, How long is the Autoflower seedling stage class 12 biology CBSE, Differentiate between the Western and the Eastern class 9 social science CBSE, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 12. Nutrients can be shown to move between different plants through the fungal network. Around 90% of terrestrial plants rely on mycorrhizal fungi for mineral nutrients (e.g., phosphorus), and the fungus gets nutrients generated by the plant in exchange. and receives water and/or nutrients in return.
The association is sometimes mutualistic. Hint: Mycorrhiza is the relation between the root of the plant and the fungus with mutual benefits, and they are divided into ecto and endo mycorrhizae types. Brussels sprouts, cabbage/kale, carnation, cauliflower, collards, cranberry, heath, Both soluble and i Ans. The significance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi includes alleviation of salt stress and its beneficial effects on plant growth and productivity. Among symbiotic fungi, those that enter into mycorrhizal relationships and those that enter into relationships with algae to form lichens (see below Form and function of lichens) are probably the best-known. During the winter, when the days are shorter and the amount of light available is decreased, certain plants generate little or no nutrients and must rely on fungus for sugars, nitrogenous compounds, and other nutrients that the fungi may take from waste items in the soil. Milk vine weed is being eradicated from citrus with class 12 biology CBSE, What will be the amount of DNA in a pollen grain if class 12 biology CBSE, Maximum genetic diversity of crop plants occurs where class 12 biology CBSE, Give one means of requiring the ability to detect class 12 biology CBSE, How is fructose a reducing sugar class 12 biology CBSE, How long is the Autoflower seedling stage class 12 biology CBSE, Differentiate between the Western and the Eastern class 9 social science CBSE, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 12. Nutrients can be shown to move between different plants through the fungal network. Around 90% of terrestrial plants rely on mycorrhizal fungi for mineral nutrients (e.g., phosphorus), and the fungus gets nutrients generated by the plant in exchange. and receives water and/or nutrients in return. 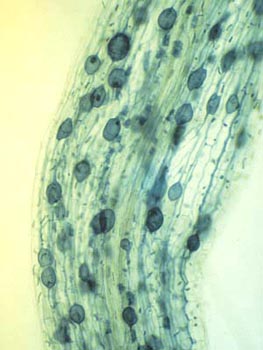 Only 5-10% of terrestrial plant species have ectomycorrhizal fungi.
Only 5-10% of terrestrial plant species have ectomycorrhizal fungi.  The mycorrhizal latifolia). needed. [51] The introduction of alien mycorrhizal plants to nutrient-deficient ecosystems puts indigenous non-mycorrhizal plants at a competitive disadvantage. This type of relationship has been The most well-known symbiotic fungus is those that develop mycorrhizal associations and those that generate lichens by forming partnerships with algae. In some cases the hyphae may also penetrate the plant cells, in which case the mycorrhiza is called an ectendomycorrhiza. ; Deslippe, J.R.; Philip, L.J. rotation may influence the root-fungi combination. Table 1. Ascomycota: It is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that forms the subkingdom Dikarya with the Basidiomycota. Arbutoid endomycorrhizas (subgroup of Ericoid), Monotropoid endomycorrhizas (subgroup These associations have been found to assist in plant defense both above and belowground. Members of the genera Russula, Clitocybe, Boletus, Lactarius, Tuber, and others are common ecto-mycorrhizal fungi. [18] An expansion of several multigene families occurred in this fungus, suggesting that adaptation to symbiosis proceeded by gene duplication. Different types of fungus, usually higher fungi, make up the fungal components. Grasshoppers of the Cherokee Nation in Northeast Oklahoma, Small Flock Biosecurity for Prevention of Avian Influenza, Beginning Honey Beekeeping Equipment and Associated Costs, Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Increased drought and salinity stress tolerance, Increased crop yield with enhanced flowering. This relationship is a natural infection The trees and their seedlings can use the fungal mycelium to exchange nutrients and chemical messages.
The mycorrhizal latifolia). needed. [51] The introduction of alien mycorrhizal plants to nutrient-deficient ecosystems puts indigenous non-mycorrhizal plants at a competitive disadvantage. This type of relationship has been The most well-known symbiotic fungus is those that develop mycorrhizal associations and those that generate lichens by forming partnerships with algae. In some cases the hyphae may also penetrate the plant cells, in which case the mycorrhiza is called an ectendomycorrhiza. ; Deslippe, J.R.; Philip, L.J. rotation may influence the root-fungi combination. Table 1. Ascomycota: It is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that forms the subkingdom Dikarya with the Basidiomycota. Arbutoid endomycorrhizas (subgroup of Ericoid), Monotropoid endomycorrhizas (subgroup These associations have been found to assist in plant defense both above and belowground. Members of the genera Russula, Clitocybe, Boletus, Lactarius, Tuber, and others are common ecto-mycorrhizal fungi. [18] An expansion of several multigene families occurred in this fungus, suggesting that adaptation to symbiosis proceeded by gene duplication. Different types of fungus, usually higher fungi, make up the fungal components. Grasshoppers of the Cherokee Nation in Northeast Oklahoma, Small Flock Biosecurity for Prevention of Avian Influenza, Beginning Honey Beekeeping Equipment and Associated Costs, Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Increased drought and salinity stress tolerance, Increased crop yield with enhanced flowering. This relationship is a natural infection The trees and their seedlings can use the fungal mycelium to exchange nutrients and chemical messages.
The Orchidaceae are notorious as a family in which the absence of the correct mycorrhizae is fatal even to germinating seeds. within a week, while others may take as long as a month. Get all the important information related to the NEET UG Examination including the process of application, important calendar dates, eligibility criteria, exam centers etc. Most soilless media does not contain mycorrhizae, so they could be incorporated if [40], AMF was also significantly correlated with soil biological fertility variables such as soil microbial communities and associated disease suppressiveness. However early observers simply recorded the fact without investigating the relationships between the two organisms. [3], A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules such as sugars by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus, and the fungus supplies to the plant water and mineral nutrients, such as phosphorus, taken from the soil. It is however different from ericoid mycorrhiza and resembles ectomycorrhiza, both functionally and in terms of the fungi involved. In comparison to the ectomycorrhizal, it is a more invasive connection. Endomycorrhiza: Endomycorrhizae, on the other hand, are present in over 80% of existing plant species, including most vegetables, grasses, flowers, and fruit trees, as well as crops and greenhouse plants. Simard, S.W. Another form of immobilisation is when nutrients are locked up in organic matter that is slow to decay, such as wood, and some mycorrhizal fungi act directly as decay organisms, mobilising the nutrients and passing some onto the host plants; for example, in some dystrophic forests, large amounts of phosphate and other nutrients are taken up by mycorrhizal hyphae acting directly on leaf litter, bypassing the need for soil uptake. The host plant releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that attract the insect's predators. Ericaceous Mycorrhizae: Ericaceous mycorrhizae can be found on plants in the Ericales order and in acidic, unfriendly conditions. Mycorrhizal symbiosis (1st ed.). There is no periradical phase and the extraradical phase consists of sparse hyphae that don't extend very far into the surrounding soil. Ectomycorrhizas, or EcM, are symbiotic associations between the roots of around 10% of plant families, mostly woody plants including the birch, dipterocarp, eucalyptus, oak, pine, and rose[9] families, orchids,[10] and fungi belonging to the Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, and Zygomycota. [31] Thus, many plants are able to obtain phosphate, without using soil as a source. During winter, when day length is shortened and exposure to sunlight is reduced, some plants produce few or no nutrients and thus depend on fungi for sugars, nitrogenous compounds, and other nutrients that the fungi are able to absorb from waste materials in the soil. Product storage temperature should not exceed 140 F or be colder than 40 F. Heavy phosphorus, nitrogen and zinc applications will inhibit mycorrhizal infection. [30], Unaided plant roots may be unable to take up nutrients that are chemically or physically immobilised; examples include phosphate ions and micronutrients such as iron. Ectomycorrhizae are fungi that are only externally associated with the plant root, whereas endomycorrhizae form their associations within the cells of the host. Some Basidiomycota, on the other hand, are obligatory asexual reproducers. The growth of a thick hyphal sheath encircling the roots surface can also be used to identify ectomycorrhizal. With approximately 64,000 species, it is the biggest phylum of Fungi. can be found in most soils naturally, so it might not be necessary to purchase mycorrhizae. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF or AM), or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. area, but rates can be as little as 1 teaspoon or 50 milliliter, if using a liquid Arbutoid Mycorrhiza: Arbutoid mycorrhizae are endomycorrhizal fungi that resemble ectomycorrhizal fungi in appearance. of a plants root system in which the plant supplies the fungus with sugars and carbon Should I Buy (or Retain) Stockers to Graze Wheat Pasture? Arbuscular mycorrhizas are found in 85% of all plant families, and occur in many crop species. By sharing the products it absorbs from the soil with its plant host, a fungus can keep its host alive. [53] One study discovered the existence of Suillus luteus strains with varying tolerance of zinc. ; Beiler, K.J. However, irrigation, harvesting and crop Mycorrhizae and climate change refers to the effects of climate change on mycorrhizae, a fungus which forms an endosymbiotic relationship between with a vascular host plant[54] by colonizing its roots, and the effects brought on by climate change. [47], Research has shown that plants connected by mycorrhizal fungi can use these underground connections to produce and receive warning signals. Ecto-mycorrhizal associations are formed by a variety of forest trees, including conifers such as Pinus, Cedrus, and Abies, as well as deciduous non-conifers such as oak, beech, and birch. "Les organes vgtatifs de, Effect of climate change on plant biodiversity, Mycorrhizal fungi and soil carbon storage, Plant to plant communication via mycorrhizal networks, "Four hundred-million-year-old vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae", "Orchids and fungi: An unexpected case of symbiosis", "Evolution and host specificity in the ectomycorrhizal genus Leccinum", "Pine microsatellite markers allow roots and ectomycorrhizas to be linked to individual trees", "Ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity: separating the wheat from the chaff", "Net transfer of carbon between ectomycorrhizal tree species in the field", Some plants may depend more on friendly fungi than own leaves: Study, "Plants and fungi together could slow climate change", "Mycorrhizas and nutrient cycling in ecosystemsa journey towards relevance?
[41] Furthermore, AMF was significantly correlated with soil physical variable, but only with water level and not with aggregate stability. [29] The structure of arbuscular mycorrhizas has been highly conserved since their first appearance in the fossil record,[5] with both the development of ectomycorrhizas, and the loss of mycorrhizas, evolving convergently on multiple occasions. This article gives you an insight into the zoological parks, the advantages and disadvantages of zoos and much more. Bruce Dunn, Richard Leckie, Hardeep Singh. They have a simple intraradical (growth in cells) phase, consisting of dense coils of hyphae in the outermost layer of root cells. between a fungus and the roots of its host plant. The mycelium of the mycorrhizal fungus can, however, access many such nutrient sources, and make them available to the plants they colonize. Different forms for the association are detailed in the next section. Carbon has been shown to move from paper birch trees into Douglas-fir trees thereby promoting succession in ecosystems. Some fungi can colonize new roots
[9], Associations of fungi with the roots of plants have been known since at least the mid-19th century.
solution. This genome analysis revealed the dual saprotrophic and biotrophic lifestyle of the mycorrhizal fungus that enables it to grow within both soil and living plant roots. [38], Mycorrhizal plants are often more resistant to diseases, such as those caused by microbial soil-borne pathogens. In a study by Klironomos and Hart, Eastern White Pine inoculated with L. bicolor was able to derive up to 25% of its nitrogen from springtails. in relation to the root tissues of the plant with endomycorrhiza producing hyphae
This relationship was noted when mycorrhizal fungi were unexpectedly found to be hoarding nitrogen from plant roots in times of nitrogen scarcity. [citation needed] Their hyphae penetrate into the root cells and form pelotons (coils) for nutrient exchange.
[26], Recent research into ectomycorrhizal plants in boreal forests has indicated that mycorrhizal fungi and plants have a relationship that may be more complex than simply mutualistic. Mycorrhizal fungi can be purchased at garden centers, nurseries or online [50] The absence of mycorrhizal fungi can also slow plant growth in early succession or on degraded landscapes. The ascus sac, a tiny sexual structure in which nonmotile spores termed ascospores are produced, i Ans. Agarics and gasteromycetes are common basidiomycetes. Pine trees inoculated with Pisolithus tinctorius planted in several contaminated sites displayed high tolerance to the prevailing contaminant, survivorship and growth. A significant number of fungi infect plant roots by developing a mycorrhizal relationship with the plants. [44][45][46] Within lineage-specific genes those coding for symbiosis-regulated secreted proteins showed an up-regulated expression in ectomycorrhizal root tips suggesting a role in the partner communication. Ans. [36], The mechanisms by which mycorrhizae increase absorption include some that are physical and some that are chemical.
Mycorrhiza is a non-disease-causing relationship in which a fungus infiltrates the root and absorbs nutrients. The hyphae of orchidaceous mycorrhiza penetrate the roots cells and generate hyphal coils, or pelotons, which are nutrient exchange sites, after the seed coat ruptures and roots begin to emerge. Learn more about the grasshoppers of the Cherokee Nation in Northeast Oklahoma. because the hyphae increase the root surface area of absorption from soil. Difference between Statutory and Non-Statutory Bodies. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas[1]) is a mutual symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The Hartig Net is an intercellular surface that defines ectomycorrhizal interactions. Orchid Mycorrhiza: Certain orchids are unable to photosynthesize until they reach the seedling stage. [2] The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, its root system. Arbuscular mycorrhizae Ans. Mycorrhizas have been found to excrete enzymes that are toxic to soil borne organisms such as nematodes. Ectomycorrhizae inside the roots and ectomycorrhiza-producing hyphae outside the roots. Mycorrhizas are located in the roots of vascular plants, but mycorrhiza-like associations also occur in bryophytes[4] and there is fossil evidence that early land plants that lacked roots formed arbuscular mycorrhizal associations. Chemically, the cell membrane chemistry of fungi differs from that of plants. L. bicolor is lacking enzymes involved in the degradation of plant cell wall components (cellulose, hemicellulose, pectins and pectates), preventing the symbiont from degrading host cells during the root colonisation. In return, the plant gains the benefits of the mycelium's higher absorptive capacity for water and mineral nutrients, partly because of the large surface area of fungal hyphae, which are much longer and finer than plant root hairs, and partly because some such fungi can mobilize soil minerals unavailable to the plants' roots. Step by step video & image solution for [object Object] by Biology experts to help you in doubts & scoring excellent marks in Class 11 exams. [9] The hyphae of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi produce the glycoprotein glomalin, which may be one of the major stores of carbon in the soil. 2012. Products the interior of the cell), but invaginate the cell membrane. [23], Ericoid mycorrhizas are the third of the three more ecologically important types. One form of such immobilization occurs in soil with high clay content, or soils with a strongly basic pH. Ectomycorrhizas consist of a hyphal sheath, or mantle, covering the root tip and a Hartig net of hyphae surrounding the plant cells within the root cortex. The plants connected by mycorrhizal fungi are also prompted to produce identical VOCs that protect the uninfected plants from being targeted by the insect. ", "Forests trapped in nitrogen limitation - an ecological market perspective on ectomycorrhizal symbiosis", "Evolutionary history of plant hosts and fungal symbionts predicts the strength of mycorrhizal mutualism", "Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi contribute to phosphorus uptake by wheat grown in a phosphorus-fixing soil even in the absence of positive growth responses", "Nitrogen Fixation Associated with Suillus tomentosus Tuberculate Ectomycorrhizae on Pinus contorta var. [41] Thus, ecosystem services provided by AMF may depend on the soil microbiome. These are Outside the root, ectomycorrhizal extramatrical mycelium forms an extensive network within the soil and leaf litter. Ans. from companies like Plant Success, Bio Organics, Soil Moist or ARBICO Organics. extending into the spaces between the cortical cells. Many orchids form mycorrhizae with species of Rhizoctonia that provide seedlings of the orchid host with carbohydrate obtained by degradation of organic matter in the soil. hyphae are smaller in diameter compared to plant roots and can reach areas unavailable
can reproduce with ideal circumstances, such as adding mulch and compost. In this chapter we will discuss zygote definition, formation of zygote, development of zygote and much more.At last we will discuss some important questions related to this topic. are several thousand different species of mycorrhiza fungi. Climate change is any lasting effect in weather or temperature. latifolia", "Botany online: Interactions - Plants - Fungi - Parasitic and Symbiotic Relations - Mycorrhiza", "Suppression of the activity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by the soil microbiota", "Salinity stress alleviation using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. The mantle is the term for this. Researchers argue that some mycorrhizae distribute nutrients based upon the environment with surrounding plants and other mycorrhizae. This is Download our apps to start learning, Call us and we will answer all your questions about learning on Unacademy. It is important to note that a good indicator of climate change is global warming, though the two are not analogous. Both soluble and insoluble nutrients can be absorbed by fungal hyphae. Mycorrhiza is a non-disease-producing association in which the fungus invades the root to absorb nutrients. The main benefit mycorrhizal fungi provide is access to large amount of water and around since plants began growing on land about 400 to 500 million years ago. Ans. [35], Suillus tomentosus, a basidiomycete fungus, produces specialized structures known as tuberculate ectomycorrhizae with its plant host lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta var. Partial list of plants that benefit from the use of ectomycorrhizal fungi. [60], Disease, drought and salinity resistance and its correlation to mycorrhizae. Mycorrhizal fungi can be found as granular, powder or in concentrated solution. By Courtney Bir, Justin Talley and JJ Jones. [39] More recent studies have shown that mycorrhizal associations result in a priming effect of plants that essentially acts as a primary immune response. of cuttings or plugs during transplanting, incorporating into the media or the soil Carbon has been observed moving from paper birch trees to Douglas-fir trees, encouraging ecological succession. Ectomycorrhizal fungi, which account for about Application rates vary by product and application Some Ascomycota species, however, are asexual, meaning they lack a sexual cycle and so do not produce asci or ascospores. "Fungal Biology Review" 26: 39-60. The fungal network has been proven to transport nutrients between plants. [citation needed] It differs from ectomycorrhiza in that some hyphae actually penetrate into the root cells, making this type of mycorrhiza an ectendomycorrhiza.
Most commercial mycorrhizal fungi products do not require any reapplication; [59] Further research was carried out by Albert Bernhard Frank, who introduced the term mycorrhiza in 1885. [5], Mycorrhizas are present in 92% of plant families studied (80% of species),[9] with arbuscular mycorrhizas being the ancestral and predominant form,[9] and the most prevalent symbiotic association found in the plant kingdom. [12] Thousands of ectomycorrhizal fungal species exist, hosted in over 200 genera. By Alex J. Harman, W. Wyatt Hoback, Tom A. Royer. Although salinity can negatively affect arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, many reports show improved growth and performance of mycorrhizal plants under salt stress conditions. Ans. As a result of this inoculation, defense responses are stronger in plants with mycorrhizal associations. The structure of the arbuscules greatly increases the contact surface area between the hypha and the cell cytoplasm to facilitate the transfer of nutrients between them. It is important to note that mycorrhizae huckleberry, mustard, protea, rhododendron, sedge and spinach. The inoculant Mycorrhizal fungi develop a mutualistic parasitism in which both the plant and the fungus profit from the relationship. At around 400million years old, the Rhynie chert contains an assemblage of fossil plants preserved in sufficient detail that mycorrhizas have been observed in the stems of Aglaophyton major. Basidiospores are these specialized spores. 3 percent of mycorrhizhae, are more advanced and benefit mainly woody and tree species Learn about equipment necessary to begin beekeeping and the options and costs of the various items. Ascomycetes truffles have the ability to form associations with pine trees. Application of mycorrhizal fungi in production can be conducted as direct infection About 90 percent of land plants rely on mycorrhizal fungi, especially for mineral nutrients (i.e., phosphorus), and in return the fungus receives nutrients formed by the plant. There are two main types of mycorrhiza: ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae. [19], Endomycorrhizas are variable and have been further classified as arbuscular, ericoid, arbutoid, monotropoid, and orchid mycorrhizas.[20]. Fungi have been found to have a protective role for plants rooted in soils with high metal concentrations, such as acidic and contaminated soils. Academic Press, London. Morels, truffles, brewers yeast and bakers yeast, dead mans fingers, and cup fungus are all examples of sac fungi. In such a relationship, both the plants themselves and those parts of the roots that host the fungi, are said to be mycorrhizal. They create a fungal sheath around the plants roots, but the arbutoid mycorrhizas hyphae enter the cortical cells of plant roots, distinguishing it from ectomycorrhizal fungi. Other orchids are completely photon-deficient. Smith 1983. Hence it can be concluded that the most well-known symbiotic fungus is those that develop mycorrhizal associations and those that generate lichens by forming partnerships with algae. [22] Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi have (possibly) been asexual for many millions of years and, unusually, individuals can contain many genetically different nuclei (a phenomenon called heterokaryosis). Sac fungi or ascomycetes are the popular names for its members. Among the mycorrhizal fungi are boletes, whose mycorrhizal relationships with larch trees (Larix) and other conifers have long been known. Arbuscular mycorrhizas are formed only by fungi in the division Glomeromycota. Partial list of plants that benefit from endomycorrhizae. [25], All orchids are myco-heterotrophic at some stage during their lifecycle and form orchid mycorrhizas with a range of basidiomycete fungi. The arbutoid mycorrhizas hyphae enter the cortical cells of plant roots, distinguishing it from ectomycorrhizal fungi. These plants are heterotrophic or mixotrophic and derive their carbon from the fungus partner. Ectomycorrhizae and Endomycorrhizae are two different forms of symbiotic connections between fungus and higher plant roots. By [29] The carbohydrates are translocated from their source (usually leaves) to root tissue and on to the plant's fungal partners. Basidiomycota: Basidiomycota is one of two great divisions that make up the subkingdom Dikarya (commonly referred to as the upper fungi ) within the kingdom Fungi, along with Ascomycota. Physically, most mycorrhizal mycelia are much smaller in diameter than the smallest root or root hair, and thus can explore soil material that roots and root hairs cannot reach, and provide a larger surface area for absorption. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Outside of the root cells, mycorrhizal fungi create hyphal coils, which dramatically increase root volume. [7][8] Endomycorrhiza includes arbuscular, ericoid, and orchid mycorrhiza, while arbutoid mycorrhizas can be classified as ectoendomycorrhizas. Ericoid mycorrhiza does not produce arbuscules, despite the fact that it penetrates and invaginates the root cells. Fungicides should be avoided, since mycorrhizae fungi are a type of fungi. Laccaria bicolor, an ectomycorrhizal fungus, has been discovered to attract and kill springtails in order to collect nitrogen, which may subsequently be passed to the mycorrhizal host plant. In some lowland forests, the soil contains an abundance of mycorrhizal fungi, resulting in mycelial networks that connect the trees together. Endomycorrhizal connections are defined by the fungis penetration of the cortical cells and the development of arbuscules and vesicles in the cortical cells. Basidiomycetes are the members of this fungus. These structures have been shown to host nitrogen fixing bacteria which contribute a significant amount of nitrogen and allow the pines to colonize nutrient-poor sites. Monotropoid mycorrhizas form a special category. [28], The mycorrhizal mutualistic association provides the fungus with relatively constant and direct access to carbohydrates, such as glucose and sucrose. nutrients (particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, zinc, manganese and copper). The most commonly found beneficial insects, their role in pest control and how to use these insects within Oklahoma ecosystems. By contrast, L. bicolor possesses expanded multigene families associated with hydrolysis of bacterial and microfauna polysaccharides and proteins. growing in containers. The first genomic sequence for a representative of symbiotic fungi, the ectomycorrhizal basidiomycete L. bicolor, was published in 2008. [8], Ericoid mycorrhizas have also been shown to have considerable saprotrophic capabilities, which would enable plants to receive nutrients from not-yet-decomposed materials via the decomposing actions of their ericoid partners. The use of mycorrhizal [48][49] Specifically, when a host plant is attacked by an aphid, the plant signals surrounding connected plants of its condition. The Hartig Net is an intercellular surface that defines ectomycorrhizal interactions. however, others recommend additional applications after several weeks. of the plants in the world (Table 1). Fungal hyphae have the ability to absorb nutrients and water all the way along their length. [citation needed], Mycorrhizal fungi form a mutualistic relationship with the roots of most plant species. [34], In some more complex relationships, mycorrhizal fungi do not just collect immobilised soil nutrients, but connect individual plants together by mycorrhizal networks that transport water, carbon, and other nutrients directly from plant to plant through underground hyphal networks. (ECM) form a thick mantle of hyphae (mycelium) surrounding the root and root tip, A review", "Interplant signalling through hyphal networks", "Overview: Weather, Global Warming and Climate Change", "An obligately endosymbiotic mycorrhizal fungus itself harbors obligately intracellular bacteria", "Hidden Partners: Mycorrhizal Fungi and Plants", Re-publication of a translation of 'The vegetative organs of, "ber die auf Wurzelsymbiose beruhende Ernhrung gewisser Bume durch unterirdische Pilze", Mohamed Hijri: A simple solution to the coming phosphorus crisis, Mycorrhizal Associations: The Web Resource, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Mycorrhiza&oldid=1096787390, Short description is different from Wikidata, Pages using multiple image with manual scaled images, Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text, Articles with unsourced statements from November 2014, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 6 July 2022, at 16:29.