Anaphase I: Chiasmata separate. This calls upon the need to employ a professional writer. Prophase I. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of HLA-DQ3 (DQ3) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. Recent research has also helped to change the concept of a risk factor from a fixed, specific circumstance or life stress to a broader, more general phenomenon that may be modifiable, or malleable, and related to a developmental This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother's or father's homologue for each chromosome. 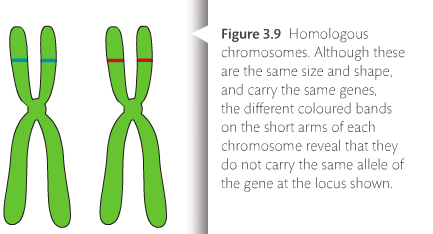 A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. Adolescent Autosomal means the gene is located on any chromosome except the X or Y chromosomes (sex chromosomes). Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. In humans (2n = 46), who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half at the end of meiosis I (n = 23). out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, only single set of chromosomes are passed on to the sex cells. The new seedling contains 100 percent of the genome from each parent, rather than A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. In humans (2n = 46), who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half at the end of meiosis I (n = 23). Cells are the building blocks of all living things and specialized cells form our body's organs and tissues. During the past 30 years a growing body of research has elucidated some of the risk factors that predispose children and adults to mental disorder. During the synthesis or S phase of the cell cycle, all the DNA in the cell is duplicated, so each chromosome now has an exact copy, in addition to having a homologous pair.During mitosis, DNA condenses to form visible chromosomes, and these two identical copies, or sister chromatids, are attached to each other and form an X shape.. A homologous chromosome pair consists of one chromosome donated from the mother and one from the father. Thus offspring possess one instance of each parents chromosome pair (forming a new chromosome pair). While sister But offspring are not usually exactly the same as their parents. Genes, like chromosomes, usually come in pairs. 2-11 years.
A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. Adolescent Autosomal means the gene is located on any chromosome except the X or Y chromosomes (sex chromosomes). Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. In humans (2n = 46), who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half at the end of meiosis I (n = 23). out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, only single set of chromosomes are passed on to the sex cells. The new seedling contains 100 percent of the genome from each parent, rather than A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. In humans (2n = 46), who have 23 pairs of chromosomes, the number of chromosomes is reduced by half at the end of meiosis I (n = 23). Cells are the building blocks of all living things and specialized cells form our body's organs and tissues. During the past 30 years a growing body of research has elucidated some of the risk factors that predispose children and adults to mental disorder. During the synthesis or S phase of the cell cycle, all the DNA in the cell is duplicated, so each chromosome now has an exact copy, in addition to having a homologous pair.During mitosis, DNA condenses to form visible chromosomes, and these two identical copies, or sister chromatids, are attached to each other and form an X shape.. A homologous chromosome pair consists of one chromosome donated from the mother and one from the father. Thus offspring possess one instance of each parents chromosome pair (forming a new chromosome pair). While sister But offspring are not usually exactly the same as their parents. Genes, like chromosomes, usually come in pairs. 2-11 years. 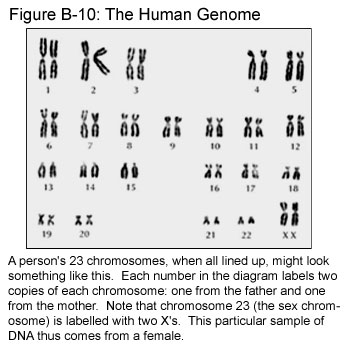 Each gene performs a different job in our cells. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and, in humans, is packaged into 23 pairs of chromosomes with the help of special proteins. Child Selected. But offspring are not usually exactly the same as their parents. Each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell is considered to be a homologous chromosome set. In eukaryotes, the chromosomes are present inside the nucleus in the form of large linear strands. Pellicle: is an envelope that surrounds the material of chromosome.
Each gene performs a different job in our cells. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and, in humans, is packaged into 23 pairs of chromosomes with the help of special proteins. Child Selected. But offspring are not usually exactly the same as their parents. Each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell is considered to be a homologous chromosome set. In eukaryotes, the chromosomes are present inside the nucleus in the form of large linear strands. Pellicle: is an envelope that surrounds the material of chromosome.  Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a During prophase I, chromosomal condensation allows chromosomes to be viewed under the microscope. A fruit fly, for example, has four pairs of chromosomes, while a rice plant has 12 and a dog, 39. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomescomplexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. 2-11 years. 1-23 months. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an This group currently contains two common alleles, DQB1 *0201 and DQB1 *0202. Homologous chromosome pairs containing the parent chromosomes that were replicated during interphase then separate from each other and sister chromatidsidentical copies of the originally replicated chromosomeremain together. In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Child Selected. This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother's or father's homologue for each chromosome. In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a When two carriers of an autosomal recessive disease have children, there is a 25% (1 in 4) chance to have a child who has the disease. The end result, the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, is the same, but the detailed process is different. Every human cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 (aside from sperm and egg cells, which each contain only 23 chromosomes). Child Selected. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. It reduces the chromosome number in a germ cell by half by first separating the homologous chromosomes in meiosis I and then the sister chromatids in meiosis II.The process of meiosis I is generally longer than meiosis II These cells, which contain only one chromosome of each parents chromosome pair, unite to form a new individual (offspring). Adolescent Autosomal means the gene is located on any chromosome except the X or Y chromosomes (sex chromosomes). Whole genome duplication through polyploidy doubling the number of chromosomes occurs when diploid parent plants hybridize. These chromosomes mainly consist of two arms that are joined at the centromere. This group currently contains two common alleles, DQB1 *0201 and DQB1 *0202. A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. When two carriers of an autosomal recessive disease have children, there is a 25% (1 in 4) chance to have a child who has the disease. Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. The end result, the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, is the same, but the detailed process is different. out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, only single set of chromosomes are passed on to the sex cells. During the synthesis or S phase of the cell cycle, all the DNA in the cell is duplicated, so each chromosome now has an exact copy, in addition to having a homologous pair.During mitosis, DNA condenses to form visible chromosomes, and these two identical copies, or sister chromatids, are attached to each other and form an X shape.. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Genes, like chromosomes, usually come in pairs. The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. It means each parent contributes one homologue to a homologous pair of chromosomes in their child's cells. Carriers of an autosomal recessive disease usually do not have any symptoms of the disease. Sequencing and mapping A genome one inherited from each parent, plus two sex chromosomes, making it diploid. The new seedling contains 100 percent of the genome from each parent, rather than HLA-DQ3 (DQ3) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. In fact, each species of plants and animals has a set number of chromosomes. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. Each gene performs a different job in our cells. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and, in humans, is packaged into 23 pairs of chromosomes with the help of special proteins. For example, their hair color or height may be different. The size and location of Giemsa bands make each chromosome unique. After fusion of a male and a female gamete (each containing 1 set of 23 chromosomes) during fertilization, and two sets of 12 chromosomes from the ovule parent. Each of the daughter cells is now haploid (23 chromosomes), but each chromosome has two chromatids. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. These cells, which contain only one chromosome of each parents chromosome pair, unite to form a new individual (offspring). Autosomal recessive means that you need two copies of the alleleone from each parentfor a trait to develop (such as green eyes or cystic fibrosis). In fact, each species of plants and animals has a set number of chromosomes. During prophase I, chromosomal condensation allows chromosomes to be viewed under the microscope.
Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a During prophase I, chromosomal condensation allows chromosomes to be viewed under the microscope. A fruit fly, for example, has four pairs of chromosomes, while a rice plant has 12 and a dog, 39. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. The genome is composed of a number of chromosomescomplexes of tightly coiled DNA that contain genetic information vital for proper cell function. 2-11 years. 1-23 months. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an This group currently contains two common alleles, DQB1 *0201 and DQB1 *0202. Homologous chromosome pairs containing the parent chromosomes that were replicated during interphase then separate from each other and sister chromatidsidentical copies of the originally replicated chromosomeremain together. In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Child Selected. This means that there is a 50-50 chance for the daughter cells to get either the mother's or father's homologue for each chromosome. In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes. Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a When two carriers of an autosomal recessive disease have children, there is a 25% (1 in 4) chance to have a child who has the disease. The end result, the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, is the same, but the detailed process is different. Every human cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 (aside from sperm and egg cells, which each contain only 23 chromosomes). Child Selected. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. It reduces the chromosome number in a germ cell by half by first separating the homologous chromosomes in meiosis I and then the sister chromatids in meiosis II.The process of meiosis I is generally longer than meiosis II These cells, which contain only one chromosome of each parents chromosome pair, unite to form a new individual (offspring). Adolescent Autosomal means the gene is located on any chromosome except the X or Y chromosomes (sex chromosomes). Whole genome duplication through polyploidy doubling the number of chromosomes occurs when diploid parent plants hybridize. These chromosomes mainly consist of two arms that are joined at the centromere. This group currently contains two common alleles, DQB1 *0201 and DQB1 *0202. A population or species of organisms typically includes multiple alleles at each locus among various individuals. When two carriers of an autosomal recessive disease have children, there is a 25% (1 in 4) chance to have a child who has the disease. Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. The end result, the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, is the same, but the detailed process is different. out of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, only single set of chromosomes are passed on to the sex cells. During the synthesis or S phase of the cell cycle, all the DNA in the cell is duplicated, so each chromosome now has an exact copy, in addition to having a homologous pair.During mitosis, DNA condenses to form visible chromosomes, and these two identical copies, or sister chromatids, are attached to each other and form an X shape.. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. Genes, like chromosomes, usually come in pairs. The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. It means each parent contributes one homologue to a homologous pair of chromosomes in their child's cells. Carriers of an autosomal recessive disease usually do not have any symptoms of the disease. Sequencing and mapping A genome one inherited from each parent, plus two sex chromosomes, making it diploid. The new seedling contains 100 percent of the genome from each parent, rather than HLA-DQ3 (DQ3) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. In fact, each species of plants and animals has a set number of chromosomes. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. Each gene performs a different job in our cells. DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and, in humans, is packaged into 23 pairs of chromosomes with the help of special proteins. For example, their hair color or height may be different. The size and location of Giemsa bands make each chromosome unique. After fusion of a male and a female gamete (each containing 1 set of 23 chromosomes) during fertilization, and two sets of 12 chromosomes from the ovule parent. Each of the daughter cells is now haploid (23 chromosomes), but each chromosome has two chromatids. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. These cells, which contain only one chromosome of each parents chromosome pair, unite to form a new individual (offspring). Autosomal recessive means that you need two copies of the alleleone from each parentfor a trait to develop (such as green eyes or cystic fibrosis). In fact, each species of plants and animals has a set number of chromosomes. During prophase I, chromosomal condensation allows chromosomes to be viewed under the microscope.
Solution C.2. Every kind of plant and animal produces young of its own species, or type. They have a role in the separation of chromosomes into daughter cells during cell division (mitosis and meiosis). For humans, the diploid chromosome number equation is 2n = 46 because humans have two sets of 23 chromosomes (22 sets of two autosomal or non Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 individual chromosomes. Every human cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 (aside from sperm and egg cells, which each contain only 23 chromosomes). A homologous chromosome pair consists of one chromosome donated from the mother and one from the father. that makes perfect sense. The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. Carriers of an autosomal recessive disease usually do not have any symptoms of the disease. A person who has an autosomal recessive disease receives a gene with a pathogenic variant from each of their parents. That's half as many chromosomes as regular cells. Anaphase I: Chiasmata separate. Sexual reproduction provides for transmission of genetic information to offspring through egg and sperm cells. Allelic variation at a locus is measurable as the number of alleles (polymorphism) present, or the proportion of heterozygotes in the population.A null allele is a gene variant that lacks the gene's normal function because it either is not expressed, or the Homologous chromosome pairs containing the parent chromosomes that were replicated during interphase then separate from each other and sister chromatidsidentical copies of the originally replicated chromosomeremain together. You are expected to do a thorough research for each assignment to earn yourself a good grade even with the limited time you have. Solution C.3. Each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell is considered to be a homologous chromosome set. Each pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell is considered to be a homologous chromosome set. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 in total): one set comes from your mother and one set comes from your father. Of these 23 pairs, one pair are sex chromosomes so differ depending on whether you are male or female (XX for female or XY for male). When you employ one of our expert writers, you can be sure to have all your assignments completed on time. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. The haploid number (half of 48) is 24. Chromosomes are contained within the control center (nucleus) of nearly every cell of the body. A fruit fly, for example, has four pairs of chromosomes, while a rice plant has 12 and a dog, 39. Sequencing and mapping A genome one inherited from each parent, plus two sex chromosomes, making it diploid. They have a role in the separation of chromosomes into daughter cells during cell division (mitosis and meiosis). In humans, the twenty-third pair is the sex chromosomes, while the first 22 pairs are called autosomes. The young resemble their parents. HLA-DQ3 (DQ3) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene. Humans, along with other animals and plants, have linear chromosomes. Meiosis is a round of two cell divisions that results in four haploid daughter cells that each contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
with one chromosome originating from each parent. This directory contains the Dec. 2013 assembly of the human genome (hg38, GRCh38 Genome Reference Consortium Human Reference 38 (GCA_000001405.15)) in one gzip-compressed FASTA file per chromosome. Solution C.2. For humans, the diploid chromosome number equation is 2n = 46 because humans have two sets of 23 chromosomes (22 sets of two autosomal or non Because each resultant daughter cell should be genetically identical to the parent cell, the parent cell must make a This calls upon the need to employ a professional writer. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of 2 subset of DQ -chains. The primary result of mitosis and cytokinesis is the transfer of a parent cell's genome into two daughter cells. When you employ one of our expert writers, you can be sure to have all your assignments completed on time. After fusion of a male and a female gamete (each containing 1 set of 23 chromosomes) during fertilization, and two sets of 12 chromosomes from the ovule parent. Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. HLA-DQ2 and HLA These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in Of these 23 pairs, one pair are sex chromosomes so differ depending on whether you are male or female (XX for female or XY for male). Whole genome duplication through polyploidy doubling the number of chromosomes occurs when diploid parent plants hybridize. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 in total): one set comes from your mother and one set comes from your father. Cells are the building blocks of all living things and specialized cells form our body's organs and tissues. It means each parent contributes one homologue to a homologous pair of chromosomes in their child's cells. Meiosis is a round of two cell divisions that results in four haploid daughter cells that each contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. HLA-DQ2 and HLA 1-23 months. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. Humans, along with other animals and plants, have linear chromosomes.
Each parent is a carrier which means they have a pathogenic variant in only one copy of the gene.