Concentrated hydroxide solutions evolve heat when mixed with water or acids, which may cause boiling and splattering. At room temperature, ammonia is a colorless, highly irritating gas with a pungent, suffocating odor. The pH value of NH4OH lies between 7 to 10. pink in the presence of hydroxide ions or base. Battery Acid If Kb>1, then the nature of the compound is a strong base. The reaction produces an ammonium ion, which is positively charged, and a chloride ion, which is negatively charged. It is used as a cleansing agent in many household works. Furthermore, the chloride ion is known as the conjugate base of the acid, while the ammonium ion is the conjugate of the base ammonia. All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. OH-, Ammonia - Chime It appears colorless and able to irritate the eyes on direct contact. Example: Sodium hydroxide(NaOH), Barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2), Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), Lithium hydroxide (LiOH), Potassium hydroxide (KOH), etc. Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) Calculating hydronium or hydroxyl ion concentrations produced by weak acids and bases is less straight forward than for strong acids and bases. It is classified in the United States by the Food and Drug Administration as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when using the food grade version. molecule takes part in the reaction as one of the reactants. Other risks associated with long term exposure to ammonium hydroxide include central nervous system depression, ulceration of the cornea, and conjunctiva of the eyes, which can cause temporary blindness. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). The container should be swirled constantly until the pellets are dissolved to prevent them from getting stuck to the bottom where they can generate excessive heat, possibly leading to container rupture.  This table provides a simple way to interpret equilibrium constants. It can cause severe irritation on direct contact with the skin for the long term. Is it strong or weak, etc? Ammonia gas is flammable and has a narrow explosive range in air of 1525%. If youre exposed to high concentrations of the substance, it can lead to pulmonary edema or swelling of the lungs. still receive inquiries, from time-to-time about using NH4OH Hence, the ions (NH4+ and OH) are very less in number as compared to (NH3 and H2O), therefore, less number of OH ions makes the ammonium hydroxide a weak base (NH4OH) in nature or you can say, an aqueous solution of ammonia is a weak base due to fewer OH ions. Ammonia has alkaline properties and is corrosive. This means that at a given concentration, different acids and bases produce different hydronium (hydrogen) or hydroxyl ion concentrations when dissolved in water. DOI: 10.3109/15563651003627777, Division of Research Safety
It was obtained from deer antlers. The acids at the top of the list are the strongest and have the highest Ka values and the corresponding lowest pKa values, while the acids at the bottom of the list are the weakest and have the lowest Ka values and the corresponding highest pKa values. Lets check whether NH4OH fulfills the requirement for classifying as Bronsted-Lowry base or not. See Also: What is an Acid? Ammonium hydroxide is otherwise known as ammonia solution, ammonia water, ammonia liquor, or aqua ammonia. Titanium dioxide is a simple oxide of titanium thats extracted from naturally occurring minerals, namely ilmenite, rutile, and anatase. read more, Organic chemistry is somewhere between inorganic chemistry and biochemistry. leaks can pose many hazards. Ammonium hydroxide has a role as a food acidity regulator. The acidity constant (Ka) is the equilibrium constant for the reaction that produces the hydrogen ion (Arrhenius definition) or the hydronium ion (Brnsted-Lowry definition). When added to water (H2O), acetic acid (CH3COOH) donates a proton to water to produce an acetate ion (CH3COO-) and a hydronium ion (H3O+): The equilibrium constant for this reactions is. Ethylene Glycol Figure 3 shows Table 9.4 from Raymond. To Know Why NH4OH is acting as a Base? Use a container large enough for diluting the base and adding the neutralization agent. working in the lab using ammonium hydroxide, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Introduction To Organic Chemistry, A Level Chemistry Revision: Physical Chemistry Thermodynamics, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Carboxylic Acids And Derivatives, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Amino Acids, Proteins & DNA, Chemistry Apprenticeships: Pharmacy Assistant Apprenticeship, How to Unblock a Sink Using Sodium Hydroxide, 11b 13 Aston Fields Road, Whitehouse Industrial Estate, Runcorn, Cheshire, WA7 3DL. Although we can and will use NH4OH At equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants and products in a reaction stop changing. The H+ ions react with OH and forms H2O. Hydroxides slowly attack glass forming soluble silicates. Experience the RICCA difference. It may even perforate the gastrointestinal tract. Ammonia Solutions (NH3) If the waste solution does NOT contain any hazardous metals, consider elementary neutralization for alkali hydroxides, calcium hydroxide, and ammonium hydroxide: Neutralize with 1N hydrochloric acid. The strongly ionized In general, strong acids have Ka values greater than 10 and weak acids have Ka values less than 0.1. So, Is NH4OH an acid or base? Remove contaminated clothing and rinse the affected skin immediately with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes or until pain is relieved. reaction. However, this small amount of product is able to reduce the pH appreciably; in this case from 7.00 to 3.38. Most acids and bases, especially those that we we encounter in biological chemistry, are weak acids and bases. Ammonia, Ammonium Hydroxide, and Ammonium Ions: Ammonia, Ammonium Hydroxide, and Ammonium Ions are all similarly As shown in the figure, when NH3 is dissolved in water (NH3 + H2O = NH4OH), it dissociates into two ions (NH4+and OH) but the ion (NH4+) is not stable in an alkaline environment, it keeps breaking into NH3and H+. This pH value is also greater than the pH of 2.0 we observed for a 0.01M solution of HCl (see Figure 5, Part I, Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases), meaning acetic acid is less acidic than HCl. If Kb<1, then the nature of the compound is a weak base. We have already seen an example of this when we were discussing ammonia as a Brnsted-Lowry base (see Figure 1 in Part III - Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases). of a weak acid and a strongly ionized base. - Barium hydroxide, Is OH- an acid or base? What is a Base? The [H2O] concentration is left out of the denominator, because as the solvent its concentration is not measurably affected by the reaction with the acetic acid. or OH- ions in their formulas. for the neutralization of acids. The pKa is defined as -log(Ka). Neutralization Chemicals.
This table provides a simple way to interpret equilibrium constants. It can cause severe irritation on direct contact with the skin for the long term. Is it strong or weak, etc? Ammonia gas is flammable and has a narrow explosive range in air of 1525%. If youre exposed to high concentrations of the substance, it can lead to pulmonary edema or swelling of the lungs. still receive inquiries, from time-to-time about using NH4OH Hence, the ions (NH4+ and OH) are very less in number as compared to (NH3 and H2O), therefore, less number of OH ions makes the ammonium hydroxide a weak base (NH4OH) in nature or you can say, an aqueous solution of ammonia is a weak base due to fewer OH ions. Ammonia has alkaline properties and is corrosive. This means that at a given concentration, different acids and bases produce different hydronium (hydrogen) or hydroxyl ion concentrations when dissolved in water. DOI: 10.3109/15563651003627777, Division of Research Safety
It was obtained from deer antlers. The acids at the top of the list are the strongest and have the highest Ka values and the corresponding lowest pKa values, while the acids at the bottom of the list are the weakest and have the lowest Ka values and the corresponding highest pKa values. Lets check whether NH4OH fulfills the requirement for classifying as Bronsted-Lowry base or not. See Also: What is an Acid? Ammonium hydroxide is otherwise known as ammonia solution, ammonia water, ammonia liquor, or aqua ammonia. Titanium dioxide is a simple oxide of titanium thats extracted from naturally occurring minerals, namely ilmenite, rutile, and anatase. read more, Organic chemistry is somewhere between inorganic chemistry and biochemistry. leaks can pose many hazards. Ammonium hydroxide has a role as a food acidity regulator. The acidity constant (Ka) is the equilibrium constant for the reaction that produces the hydrogen ion (Arrhenius definition) or the hydronium ion (Brnsted-Lowry definition). When added to water (H2O), acetic acid (CH3COOH) donates a proton to water to produce an acetate ion (CH3COO-) and a hydronium ion (H3O+): The equilibrium constant for this reactions is. Ethylene Glycol Figure 3 shows Table 9.4 from Raymond. To Know Why NH4OH is acting as a Base? Use a container large enough for diluting the base and adding the neutralization agent. working in the lab using ammonium hydroxide, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Introduction To Organic Chemistry, A Level Chemistry Revision: Physical Chemistry Thermodynamics, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Carboxylic Acids And Derivatives, A Level Chemistry Revision: Organic Chemistry Amino Acids, Proteins & DNA, Chemistry Apprenticeships: Pharmacy Assistant Apprenticeship, How to Unblock a Sink Using Sodium Hydroxide, 11b 13 Aston Fields Road, Whitehouse Industrial Estate, Runcorn, Cheshire, WA7 3DL. Although we can and will use NH4OH At equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants and products in a reaction stop changing. The H+ ions react with OH and forms H2O. Hydroxides slowly attack glass forming soluble silicates. Experience the RICCA difference. It may even perforate the gastrointestinal tract. Ammonia Solutions (NH3) If the waste solution does NOT contain any hazardous metals, consider elementary neutralization for alkali hydroxides, calcium hydroxide, and ammonium hydroxide: Neutralize with 1N hydrochloric acid. The strongly ionized In general, strong acids have Ka values greater than 10 and weak acids have Ka values less than 0.1. So, Is NH4OH an acid or base? Remove contaminated clothing and rinse the affected skin immediately with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes or until pain is relieved. reaction. However, this small amount of product is able to reduce the pH appreciably; in this case from 7.00 to 3.38. Most acids and bases, especially those that we we encounter in biological chemistry, are weak acids and bases. Ammonia, Ammonium Hydroxide, and Ammonium Ions: Ammonia, Ammonium Hydroxide, and Ammonium Ions are all similarly As shown in the figure, when NH3 is dissolved in water (NH3 + H2O = NH4OH), it dissociates into two ions (NH4+and OH) but the ion (NH4+) is not stable in an alkaline environment, it keeps breaking into NH3and H+. This pH value is also greater than the pH of 2.0 we observed for a 0.01M solution of HCl (see Figure 5, Part I, Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases), meaning acetic acid is less acidic than HCl. If Kb<1, then the nature of the compound is a weak base. We have already seen an example of this when we were discussing ammonia as a Brnsted-Lowry base (see Figure 1 in Part III - Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases). of a weak acid and a strongly ionized base. - Barium hydroxide, Is OH- an acid or base? What is a Base? The [H2O] concentration is left out of the denominator, because as the solvent its concentration is not measurably affected by the reaction with the acetic acid. or OH- ions in their formulas. for the neutralization of acids. The pKa is defined as -log(Ka). Neutralization Chemicals.
Weak acids and weak bases produce a hydronium or hydroxyl ion concentration that is less than their total concentration. Ammonia is a weak base, according to the hydrolysis reaction: Please notice that Kb is quite small, meaning that very little ammonium and hydroxide forms in the solution. Example- Ammonia (NH3), Methylamine (CH3NH2), etc. Ammonium hydroxide is not normally a good You should also wear a face mask or a gas mask with a respirator when handling large amounts of the chemical. .jpg) Write the equilibrium constant expression, Using the equilibrium concentrations that are determined by the Virtual Lab Simulator for the 0.01M NH. A base is any compound that yields hydroxide ions (OH-) hands are from the the indicator phenolphthalein which turns Now we look for another most important acid-base theory which is the Bronsted-Lowry theory. It is used in the production of organic and inorganic chemicals. Our determined value for the pKa of acetic acid is then. Aside from water, ammonia is also soluble in chloroform, ethanol, and methanol. This reaction is observed in many reactions both in inorganic Caustic Soda Skin contact of a solution of >1% TMAH to a small area of the body surface or ingestion can be fatal. Strong or Weak - Sodium hydroxide, Is Ca(OH)2 an acid or base? It means only some of the weak base dissociates in the solution to produce OH ion, and at equilibrium, both undissociated base and their ionized product are present in the solution. Despite this, the formula for ammonium hydroxide is the same as ammonia because although the molecules separate into hydroxide and ammonium ions, the ammonium hydroxide molecules are impossible to isolate. The most commonly used chemicals are discussed in an article available here: On the basis of previously learned principles Continue to add neutralization reagent until a pH between 6 and 10 is reached. burn chemical burns acid alkali sulfuric severe conjunctival reaction injuries hydroxide sodium note ophthalmologic opacification stromal alkaline medscape ocular reactio What is pH. During read more, The A level organic chemistry syllabus includes the study of amino acids, proteins and DNA. The blog, its authors and affiliates accept no responsibility for any accident, injury or damage caused in part or directly from following the information provided on this website. How to tell if the acid or base is strong or weak? This is because the solution contains the following ions: [NH4+][OH]. In the case of a large spill of a concentrated base outside the hood, or if the spill cannot be contained, evacuate the area immediately, alerting others nearby. Adding water to concentrated bases may cause violent boiling of the solution and splashing. Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid and is characteristic of most of the biological acids we will encounter this semester. By comparison, one mole of this solution has a pH of 11.3. - Nature of Ammonium. As an example, we will use the acid/base reaction of acetic acid. you probably should say "NO". When handling large amounts (>500 mL), or when splashing is likely to occur, wear additional protection to prevent skin contact, especially when using TMAH: A face shield above splash goggles, base-resistant gloves with long cuffs, and a base-resistant apron or smock. One of the more commonly produced chemicals in the United States, Ammonia (NH3)shown in the graphic on the This means that molecular ammonia is still dominant except for in extremely dilute solutions. Xylene Its standard enthalpy of formation is -80 Kilojoules per mole. Using the Virtual Lab Simulator we were able to demonstrate how a 0.01M aqueous solution of ammonia (NH3) produces a pH of 10.6, while earlier, in the "Try This" for Part I of the Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases we saw that a 0.01M solution of the strong base NaOH produces a pH of 12.0. reverse of the neutralization reaction. Methylene Chloride Neutralize the spill first by covering it with neutralizer, then sweep up the neutralized material with an absorbent pads or a broom. Conjugate acid or base - Hydroxide, Is NH4Br an acid or base or salt? Notify me of follow-up comments by email. Other bases do not have hydroxide ions in the formula, but When handling strong bases, at a minimum wear standard laboratory attire: closed-toe shoes, long pants, a lab coat, safety glasses with side shields or splash goggles, and gloves. Acids and Bases Methylated Spirits Citric Acid (C6H8O7), Deionized Water Most detergents In pure form, it is known as anhydrous ammonia and is hygroscopic (readily absorbs moisture). Strong or Weak - Lithium hydroxide, Is KOH an acid or base? Propylene Glycol, Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) Glycerol/Glycerine/Glycerin (General Use). Note: NH4OH is a combination of NH3 + H2O, hence, not to be confused. Its not only soluble in water, but also miscible. Commonly available ammonia with soap added is known as "cloudy ammonia". In aqueous solution, ammoniadeprotonatesa small fraction of the water to giveammoniumandhydroxideaccording to the followingequilibrium: Dilute (13%) ammonia is also an ingredient of numerous cleaning agents, including many window cleaning formulas. This is based on the computation below, given the base ionisation constant: The base ionisation constant can be computed using the following expression: Since the constant is just a ratio of concentration, it doesnt have a unit, and we can substitute the given values. The blog on chemicals.co.uk and everything published on it is provided as an information resource only. It involves using the equilibrium constant for the acid or base reaction that produces the hydronium or hydroxyl ion. In other words, the concentration of OH is much smaller than thenominalammonia or ammonium hydroxide concentration. A substance doesnt necessarily have to have a hydrogen ion or a hydroxide ion to be considered either an acid or a base. But the the favor of reaction mostly lies to the left side that means large number of NH3 will present in the aqueous solution as compare to its right sided product(NH4+ and OH). Determining the hydronium ion concentrations for strong bases works similarly, but there is an extra step. Antifreeze Strong or Weak - Calcium, Is LiOH an acid or base? This solution can be prepared by mixing concentrated hydrochloric acid (37% = 12M) 1:12 with water. Hydroxides must be separated from oxidizers. Distilled Water
Write the equilibrium constant expression, Using the equilibrium concentrations that are determined by the Virtual Lab Simulator for the 0.01M NH. A base is any compound that yields hydroxide ions (OH-) hands are from the the indicator phenolphthalein which turns Now we look for another most important acid-base theory which is the Bronsted-Lowry theory. It is used in the production of organic and inorganic chemicals. Our determined value for the pKa of acetic acid is then. Aside from water, ammonia is also soluble in chloroform, ethanol, and methanol. This reaction is observed in many reactions both in inorganic Caustic Soda Skin contact of a solution of >1% TMAH to a small area of the body surface or ingestion can be fatal. Strong or Weak - Sodium hydroxide, Is Ca(OH)2 an acid or base? It means only some of the weak base dissociates in the solution to produce OH ion, and at equilibrium, both undissociated base and their ionized product are present in the solution. Despite this, the formula for ammonium hydroxide is the same as ammonia because although the molecules separate into hydroxide and ammonium ions, the ammonium hydroxide molecules are impossible to isolate. The most commonly used chemicals are discussed in an article available here: On the basis of previously learned principles Continue to add neutralization reagent until a pH between 6 and 10 is reached. burn chemical burns acid alkali sulfuric severe conjunctival reaction injuries hydroxide sodium note ophthalmologic opacification stromal alkaline medscape ocular reactio What is pH. During read more, The A level organic chemistry syllabus includes the study of amino acids, proteins and DNA. The blog, its authors and affiliates accept no responsibility for any accident, injury or damage caused in part or directly from following the information provided on this website. How to tell if the acid or base is strong or weak? This is because the solution contains the following ions: [NH4+][OH]. In the case of a large spill of a concentrated base outside the hood, or if the spill cannot be contained, evacuate the area immediately, alerting others nearby. Adding water to concentrated bases may cause violent boiling of the solution and splashing. Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid and is characteristic of most of the biological acids we will encounter this semester. By comparison, one mole of this solution has a pH of 11.3. - Nature of Ammonium. As an example, we will use the acid/base reaction of acetic acid. you probably should say "NO". When handling large amounts (>500 mL), or when splashing is likely to occur, wear additional protection to prevent skin contact, especially when using TMAH: A face shield above splash goggles, base-resistant gloves with long cuffs, and a base-resistant apron or smock. One of the more commonly produced chemicals in the United States, Ammonia (NH3)shown in the graphic on the This means that molecular ammonia is still dominant except for in extremely dilute solutions. Xylene Its standard enthalpy of formation is -80 Kilojoules per mole. Using the Virtual Lab Simulator we were able to demonstrate how a 0.01M aqueous solution of ammonia (NH3) produces a pH of 10.6, while earlier, in the "Try This" for Part I of the Elaboration - Definitions of Acids and Bases we saw that a 0.01M solution of the strong base NaOH produces a pH of 12.0. reverse of the neutralization reaction. Methylene Chloride Neutralize the spill first by covering it with neutralizer, then sweep up the neutralized material with an absorbent pads or a broom. Conjugate acid or base - Hydroxide, Is NH4Br an acid or base or salt? Notify me of follow-up comments by email. Other bases do not have hydroxide ions in the formula, but When handling strong bases, at a minimum wear standard laboratory attire: closed-toe shoes, long pants, a lab coat, safety glasses with side shields or splash goggles, and gloves. Acids and Bases Methylated Spirits Citric Acid (C6H8O7), Deionized Water Most detergents In pure form, it is known as anhydrous ammonia and is hygroscopic (readily absorbs moisture). Strong or Weak - Lithium hydroxide, Is KOH an acid or base? Propylene Glycol, Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) Glycerol/Glycerine/Glycerin (General Use). Note: NH4OH is a combination of NH3 + H2O, hence, not to be confused. Its not only soluble in water, but also miscible. Commonly available ammonia with soap added is known as "cloudy ammonia". In aqueous solution, ammoniadeprotonatesa small fraction of the water to giveammoniumandhydroxideaccording to the followingequilibrium: Dilute (13%) ammonia is also an ingredient of numerous cleaning agents, including many window cleaning formulas. This is based on the computation below, given the base ionisation constant: The base ionisation constant can be computed using the following expression: Since the constant is just a ratio of concentration, it doesnt have a unit, and we can substitute the given values. The blog on chemicals.co.uk and everything published on it is provided as an information resource only. It involves using the equilibrium constant for the acid or base reaction that produces the hydronium or hydroxyl ion. In other words, the concentration of OH is much smaller than thenominalammonia or ammonium hydroxide concentration. A substance doesnt necessarily have to have a hydrogen ion or a hydroxide ion to be considered either an acid or a base. But the the favor of reaction mostly lies to the left side that means large number of NH3 will present in the aqueous solution as compare to its right sided product(NH4+ and OH). Determining the hydronium ion concentrations for strong bases works similarly, but there is an extra step. Antifreeze Strong or Weak - Calcium, Is LiOH an acid or base? This solution can be prepared by mixing concentrated hydrochloric acid (37% = 12M) 1:12 with water. Hydroxides must be separated from oxidizers. Distilled Water 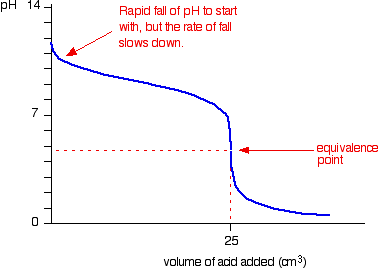 Note that the hydrolysis equation is a double replacement Ultrapure Water This reaction causes glass joints and stopcocks to freeze.. For example, in a one mole of ammonia solution, approximately 0.43% of ammonia molecules are converted into ammonium.
Note that the hydrolysis equation is a double replacement Ultrapure Water This reaction causes glass joints and stopcocks to freeze.. For example, in a one mole of ammonia solution, approximately 0.43% of ammonia molecules are converted into ammonium.