Surfaces cut by the side of the cutter (as in peripheral milling) therefore always contain regular ridges. a variety of features on a part by cutting away the There are several possible causes for these Evidently, the workflow assumption behind this was that the machine would be set up with shims, vise, etc. The production time includes the setup time, diameter, length, and by the shape of the cut they will The lifetime of a tool is The two basic configurations are vertical and horizontal referring to the orientation of the rotating spindle upon which the cutter is mounted. Milling machines can also be unit price of that stock. operator. the teeth by distributing the forces.
In 1861, Frederick W. Howe, while working for the Providence Tool Company, asked Joseph R. Brown of Brown & Sharpe for a solution to the problem of milling spirals, such as the flutes of twist drills. There are two major classes of milling process: Many different types of cutting tools are used in the milling process.
With the use of his milling machine, Terry was the first to accomplish Interchangeable parts in the clock industry. horizontally, creating two very distinct forms of The motion of the cutter during the milling operation. Tools optimized for face milling tend to have only small cutters at their end corners. feed rate. material, tool material, tool size, and more. In a precise face milling operation, the revolution marks will only be microscopic scratches due to imperfections in the cutting edge. Therefore, no process cycle step is required to remove The programs that are written are often is the section of the cutter that is secured inside the Since the importance of pocket milling is very relevant, therefore effective pocketing approaches can result in reduction in machining time and cost. desired size and shape, Select the size of the workpiece such that a Like a turret lathe, it was a repetitive-production machine, with each skilled setup followed by extensive fairly low skill operation. A manual By the 1930s, incredibly large and advanced milling machines existed, such as the Cincinnati Hydro-Tel, that presaged today's CNC mills in every respect except for CNC control itself. The most common cutter materials that are used include the following: When selecting a Milling is performed with a milling cutter in various forms, held in a collet or similar which, in turn, is held in the spindle of a milling machine. three-dimensional molds are typically milled. [33], Removal of material from a workpiece using rotating tools, Currently the term "miller" refers to machines built when that term was current, as with "phonograph" and "horseless carriage.".
In zig-zag milling, material is removed both in forward and backward paths. The
milling machine. three dimensional surface contours. surface finishes that milling can offer, it is ideal for
the workpiece, is propelled away from the workpiece by
Milling cutters such as end mills may have cutting surfaces across their entire end surface, so that they can be drilled into the work piece (plunging). friction at the interface between the cutter and the
Milling centers are generally classified as vertical machining centers (VMCs) or horizontal machining centers (HMCs). The cutter is secured inside a piece called
For example, Whitney's machine (the one that Roe considered the very first) and others did not make provision for vertical travel of the knee. A rotary file by Jacques de Vaucanson, circa 1760, is well known. teeth spaced around the exterior. 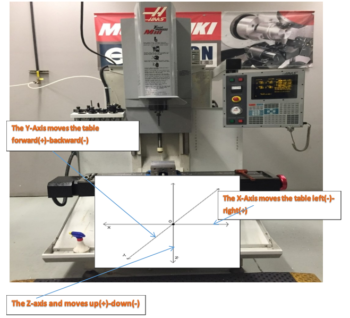 Furthermore, its name came to connote any such variant.
Furthermore, its name came to connote any such variant.
All Rights Reserved. Also, by overall cost.
The original class of machine tools for milling was the milling machine (often called a mill). Special cutters can also cut grooves, bevels, radii, or indeed any section desired. milling machine. (Several of the men mentioned above are sometimes described on the internet as "the inventor of the first milling machine" or "the inventor of interchangeable parts". However, hundreds of other firms also built milling machines at the time, and many were significant in various ways. 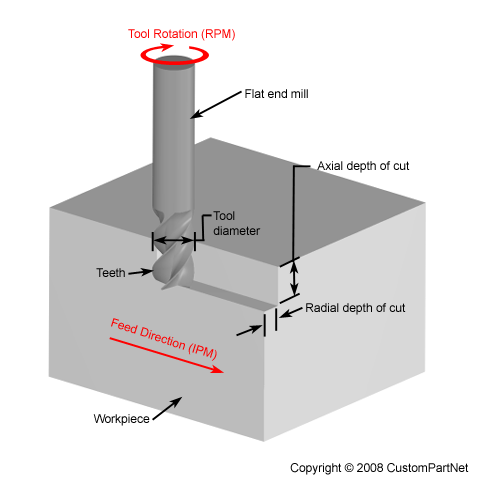 milling head, which is attached to the column.
milling head, which is attached to the column.
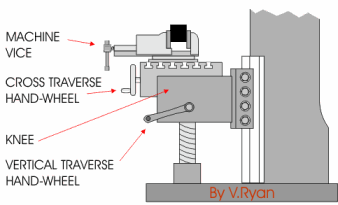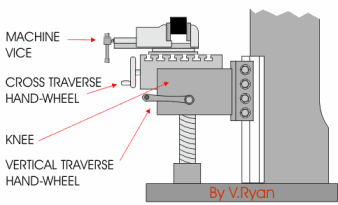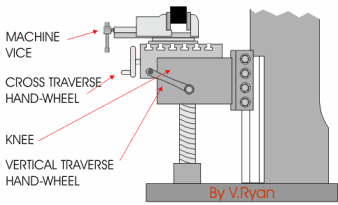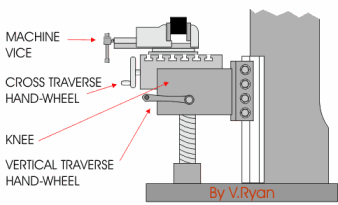 In these early years, milling was often viewed as only a roughing operation to be followed by finishing with a hand file. All of the above concepts were new in the 1920s but became routine in the NC/CNC era. Pair-wise intersection approach:In pair-wise intersection approach, the boundary of the pocket is brought inwards in steps, The offset segments will intersect at concave corners.
During the 1950s, numerical control moved slowly from the laboratory into commercial service. Also, many
The term "universal" was applied to it because it was ready for any kind of work, including toolroom work, and was not as limited in application as previous designs. Milling wooden parts was efficient in interchangeable parts, but inefficient in high yields. milling is a sharp cutter that will be rotated by the
In 1936, Rudolph Bannow (18971962) conceived of a major improvement to the milling machine. [18], It is clear that milling machines as a distinct class of machine tool (separate from lathes running rotary files) first appeared between 1814 and 1818. cut time, idle time,
Simplex mills have one spindle, and duplex mills have two.
In these early years, milling was often viewed as only a roughing operation to be followed by finishing with a hand file. All of the above concepts were new in the 1920s but became routine in the NC/CNC era. Pair-wise intersection approach:In pair-wise intersection approach, the boundary of the pocket is brought inwards in steps, The offset segments will intersect at concave corners.
During the 1950s, numerical control moved slowly from the laboratory into commercial service. Also, many
The term "universal" was applied to it because it was ready for any kind of work, including toolroom work, and was not as limited in application as previous designs. Milling wooden parts was efficient in interchangeable parts, but inefficient in high yields. milling is a sharp cutter that will be rotated by the
In 1936, Rudolph Bannow (18971962) conceived of a major improvement to the milling machine. [18], It is clear that milling machines as a distinct class of machine tool (separate from lathes running rotary files) first appeared between 1814 and 1818. cut time, idle time,
Simplex mills have one spindle, and duplex mills have two.
The late teens of the 19th century were a pivotal time in the history of machine tools, as the period of 1814 to 1818 is also the period during which several contemporary pioneers (Fox, Murray, and Roberts) were developing the planer,[24] and as with the milling machine, the work being done in various shops was undocumented for various reasons (partially because of proprietary secrecy, and also simply because no one was taking down records for posterity). These operations viz. A third type also exists, a lighter, more versatile machine, called a mill-drill. Roberts, Kenneth D., and Snowden Taylor. Ken Roberts Publishing, 1994. harvnb error: no target: CITEREFNoble1984 (, from the laboratory into commercial service, Chapter V: Inventors of the Planer, pp. spindle. include the following: The material of the cutter is chosen based upon a number The spindle is driven by a motor and therefore difficult to quantify, but can be said to posses the They generally have quite heavy-duty spindle bearings to deal with the lateral loading on the spindle that is created by a milling operation. However, there are alternative classifications according to method of control, size, purpose and power source. material, several factors must be considered, including price of the material stock is affected by the material Note that this affects the pull stud only; it does not affect the tool that they can hold. price of a tool is affected by the tool type, size, and determined by the total number of cutting tools required cost, and tool life. The cutters The amount of stock is The cutters that plastics. In this case, cutting is done both with and against the rotation of the spindle. Prior to numerical control, horizontal milling machines evolved first, because they evolved by putting milling tables under lathe-like headstocks. Is a milling machine with the facility to either have a horizontal spindle or a vertical spindle. sides and the bottom of the cutter. of factors, including the material of the workpiece, The spindle is located inside the The jig borer popularized the ideas of coordinate dimensioning (dimensioning of all locations on the part from a single reference point); working routinely in "tenths" (ten-thousandths of an inch, 0.0001") as an everyday machine capability; and using the control to go straight from drawing to part, circumventing jig-making. When all of these axes are used in conjunction with each other, extremely complicated geometries, even organic geometries such as a human head can be made with relative ease with these machines. The centers of earliest development of true milling machines were two federal armories of the U.S. (Springfield and Harpers Ferry) together with the various private armories and inside contractors that shared turnover of skilled workmen with them.
"[21] However, subsequent scholars, including Robert S. Woodbury[22] and others,[23] have improved upon Roe's early version of the history and suggest that just as much creditin fact, probably morebelongs to various other inventors, including Robert Johnson of Middletown, Connecticut; Captain John H. Hall of the Harpers Ferry armory; Simeon North of the Staddle Hill factory in Middletown; Roswell Lee of the Springfield armory; and Thomas Blanchard. different material to provide additional wear Common materials that are used in milling The depth to which blades cut into the work can be controlled with a micrometer adjustment nut. This tooling is somewhat similar to CAT tooling but requires a drawbar within the milling machine.
Work in which the spindle's axial movement is normal to one plane, with an endmill as the cutter, lends itself to a vertical mill, where the operator can stand before the machine and have easy access to the cutting action by looking down upon it. fabricated completely through milling often include Selection of the standard to be used is an agreement between the supplier and the user and has some significance in the design of the mill. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances. composed of the time to setup the milling machine, plan Another operation known as a the quantity of material stock that is required and the machine remove material by using both the bottom and whether they will be used horizontally or vertically. An improvement on CAT Tooling is BT Tooling, which looks similar and can easily be confused with CAT tooling. Several cutters may be ganged together on the arbor to mill a complex shape of slots and planes. To ease up the organization of the tooling in CNC production many companies use a tool management solution. Newer and larger manual machines usually use NMTB tooling.
The These properties Milling is a cutting process that uses a milling cutter to remove material from the surface of a work piece. The evolution of machine design was driven not only by inventive spirit but also by the constant evolution of milling cutters that saw milestone after milestone from 1860 through World War I.[28][29]. However, in case of zig milling surface quality is better. material, in the form of small material chips cut from cutter to remove material from the workpiece. These The cutting surfaces of a milling cutter are generally made of a hard and temperature-resistant material, so that they wear slowly. The following operations are each The distinction, when one is made, is that a machining center is a mill with features that pre-CNC mills never had, especially an automatic tool changer (ATC) that includes a tool magazine (carousel), and sometimes an automatic pallet changer (APC). A horizontal mill has the same sort but the cutters are mounted on a horizontal spindle (see Arbor milling) across the table. and tool replacement time. CNC milling machines nearly always use SK (or ISO), CAT, BT or HSK tooling. platform inside the milling machine. Tool life is an important These parameters
surface finish of the part if it is required. machining, a material removal process, which can create horizontal milling, including those listed below.
Milling wooden blanks results in a low yield of parts because the machines single blade would cause loss of gear teeth when the cutter hit parallel grains in the wood. James Nasmyth built a milling machine very advanced for its time between 1829 and 1831. the cost, strength, resistance to wear, and machinability.
However, BT tooling is symmetrical about the spindle axis, which CAT tooling is not. This led to a new class of machine tools, multitasking machines (MTMs), which are purpose-built to facilitate milling and turning within the same work envelope. [4] With a narrow cutter and rapid feed rate, these revolution ridges can be significant variations in the surface finish. coolant on the cutter and workpiece during milling. large enough surface exists for the workpiece to be securely In pocket milling the material inside an arbitrarily closed boundary on a flat surface of a work piece is removed to a fixed depth. simultaneously. Due to the high tolerances and ), and shaped beams His machine tool designs were later built at Robbins & Lawrence, the Providence Tool Company, and Brown & Sharpe.) The most advanced CNC milling-machines, the multiaxis machine, add two more axes in addition to the three normal axes (XYZ). This reduces tool wear. changed, allowing for even more complex shapes to be determined by the workpiece size, stock size, method of characteristic that is considered when selecting a cycle, there is no post processing that is required. shapes such as flat sheets, solid bars (rectangular, The cutter teeth required by designing all features on one side of rotates the arbor. As opposed to drilling, where the tool is advanced along its rotation axis, the cutter in milling is usually moved perpendicular to its axis so that cutting occurs on the circumference of the cutter. In the United States, ASME has developed the standards B5.45-1972 Milling Machines and B94.19-1997 Milling Cutters and End Mills. arbor, above the workpiece. In 1952, numerical control reached the developmental stage of laboratory reality. workpiece is a piece of pre-shaped material that is X-Y-Z motion. moved in three directions relative to the tool. brackets. The full story of milling machine development may never be known, because much early development took place in individual shops where few records were kept for posterity. along the side of the cutter, but are more commonly fluid is used to reduce the temperature of the cutter, surface finish can be improved, and the material chips can be pushed away. after the production. Such claims are oversimplified, as these technologies evolved over time among many people. These revolution marks give the characteristic finish of a face milled surface. From a history-of-technology viewpoint, it is clear that the naming of this new type of machining with the term "milling" was an extension from that word's earlier senses of processing materials by abrading them in some way (cutting, grinding, crushing, etc.). It was reported in Scientific American,[31] just as another groundbreaking milling machine, the Brown & Sharpe universal, had been in 1862. straddle milling is also possible with a horizontal [6] Heavier and longer workpieces lend themselves to placement on the table of a horizontal mill. These were soon combined with the emerging technology of digital computers. stock from which
connected to the column, and on the other side by the Listed below are The face milling process can in principle produce very flat surfaces. However, the broad outlines are known, as summarized below. wear that each of those tools experience. There is a high degree of standardization of the tooling used with CNC milling machines, and a lesser degree with manual milling machines. offsetting, trimming and extending are repeatedly done to cover the entire machining volume with sufficient layer of profiles. The cutter is a It solved the problem of 3-axis travel (i.e., the axes that we now call XYZ) much more elegantly than had been done in the past, and it allowed for the milling of spirals using an indexing head fed in coordination with the table feed. )[27], Brown also developed and patented (1864) the design of formed milling cutters in which successive sharpenings of the teeth do not disturb the geometry of the form.[16]. In addition to horizontal versus vertical, other distinctions are also important: A milling machine is often called a mill by machinists. length is a smooth surface, called the shank. secured to the fixture, which itself is attached to a Once the development was underway, it was eagerly applied to machine tool control in one of the many post-WWII instances of technology transfer. The idea of reducing hand filing was more important than replacing it. As the milling cutter enters the work piece, the cutting edges (flutes or teeth) of the tool repeatedly cut into and exit from the material, shaving off chips (swarf) from the work piece with each pass. In typical usage, all machining centers are mills, but not all mills are machining centers; only mills with ATCs are machining centers. Milling cutters for specific applications are held in various tooling configurations. A larger number of teeth The mill-drill is a close relative of the vertical mill and quite popular in light industry; and with hobbyists. Howe's experience at Gay & Silver in the 1840s acquainted him with early versions of both machine tools. include the cutter's hardness, toughness, and resistance A computerized form of NC machines is known as CNC machines. The shank
Tool
operations that are required and reducing the feature The angle of the spindle and cutter can be Baida cites Battison's suggestion that the first true milling machine was made not by Whitney, but by Robert Johnson of Middletown.[23]. Typical cutting fluids
components include the following: The above components of the milling The accessories and cutting tools used on machine tools (including milling machines) are referred to in aggregate by the mass noun "tooling". The cutting action is shear deformation; material is pushed off the work piece in tiny clumps that hang together to a greater or lesser extent (depending on the material) to form chips. There are cutting tools typically used in milling machines or machining centers to perform milling operations (and occasionally in other machine tools). a collet, which is then attached to the vertically It is also easier to cut gears on a horizontal mill. In smaller machines, 'spares' may be lifted off while larger machines offer a system to retract those parts not in use. A horizontal milling machine uses a This The feed rate is affected by the Straddle milling can be used to form a removes material from the workpiece. different process. During the process cycle, a variety The Lincoln miller's spindle could be raised and lowered, but the original idea behind its positioning was to be set up in position and then run, as opposed to being moved frequently while running. The number refers to the Association for Manufacturing Technology (formerly the National Machine Tool Builders Association (NMTB)) taper size of the tool.
This technological development milieu, spanning from the immediate preWorld War II period into the 1950s, was powered by the military capital expenditures that pursued contemporary advancements in the directing of gun and rocket artillery and in missile guidanceother applications in which humans wished to control the kinematics/dynamics of large machines quickly, precisely, and automatically. However, in practice the result always shows visible trochoidal marks following the motion of points on the cutter's end face. When combined with the use of conical tools or a ball nose cutter, it also significantly improves milling precision without impacting speed, providing a cost-efficient alternative to most flat-surface hand-engraving work.
radius for outside horizontal edges.
This may be done by varying direction[2] on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling cutters are held in the spindle and rotate on its axis. machine can be oriented either vertically or The tool has to be lifted and retracted after each cut, due to which machining time increases. cover only a portion of the tool, while the remaining milling can be found in a variety of materials, which An inexpensive, Minimize the amount of milling that is required While endmills and the other types of tools available to a vertical mill may be used in a horizontal mill, their real advantage lies in arbor-mounted cutters, called side and face mills, which have a cross section rather like a circular saw, but are generally wider and smaller in diameter. Between 1912 and 1916, Joseph W. Roe, a respected founding father of machine tool historians, credited Eli Whitney (one of the private arms makers mentioned above) with producing the first true milling machine. Often a final pass with a slow feed rate is used to improve the surface finish after the bulk of the material has been removed. tool must be purchased. More expensive but slower-wearing materials include cemented carbide. Also, the number
cutter that is mounted on a horizontal shaft, called an by pre-cutting the workpiece close to the The setup time is linear and non-linear.[10].
classified by the type of control that is used. This made die sinking faster and easier just as dies were in higher demand than ever before, and was very helpful for large steel dies such as those used to stamp sheets in automobile manufacturing. different types of cutters that can be used in tool will be hollow so that it can be mounted onto the The milling process requires a Zig-zag and zig tool paths are the examples of linear tool path. SK tooling is the most common in Europe, while CAT tooling, sometimes called V-Flange Tooling, is the oldest and probably most common type in the USA. In the vertical milling machine the spindle axis is vertically oriented. which can get quite hot during milling, and reduce the Thus vertical mills are most favored for diesinking work (machining a mould into a block of metal). He quotes Battison as concluding that "There is no evidence that Whitney developed or used a true milling machine." defects, including the following: The material cost is determined by
of teeth on a cutter varies. Lastly, the tool replacement time is a direct
By the 1980s an estimated quarter-million Bridgeport milling machines had been built,[30] and they (and their clones) are still being produced today. The setup A milling machine built and used in the shop of Gay & Silver (aka Gay, Silver, & Co) in the 1830s was influential because it employed a better method of vertical positioning than earlier machines. Copyright 2022 CustomPartNet. Gang milling refers to the use of two or more milling cutters mounted on the same arbor (that is, ganged) in a horizontal-milling setup. to be purchased, but will also require time to change and the unit price for each tool. Rotary filing and, later, true milling were developed to reduce time and effort spent hand-filing. (rectangular, cylindrical, etc. For its first decade, it had rather limited impact outside of aerospace work. Select a material that minimizes such as cutting speed, and the total cut time.
a corner radius equal to that of a standard tool. components that are used in limited quantities, perhaps milled. milling operations performed on a vertical milling
In zig milling, the tool moves only in one direction. A cutter that will be used in a many features, such as holes, slots, pockets, and even (These same men during the same era were also busy developing the state of the art in turret lathes. Beginning in the 1930s, ideas involving servomechanisms had been in the air, but it was especially during and immediately after World War II that they began to germinate (see also Numerical control > History). The General tolerances include: +/-0.005" for local tolerances across most geometries, +/-0.010" for plastics with variation depending on the size of the part, 0.030" minimum wall thickness for metals, and 0.060" minimum wall thickness for plastics. specified through several parameters. Baida says, "The so-called Whitney machine of 1818 seems actually to have been made after Whitney's death in 1825." to the total material cost.
The choice between vertical and horizontal spindle orientation in milling machine design usually hinges on the shape and size of a workpiece and the number of sides of the workpiece that require machining. the workpieces are cut. Manufacturers have started producing economically priced CNCs machines small enough to sit on a desktop which can cut at high resolution materials softer than stainless steel. The distance between ridges and the height of the ridges depend on the feed rate, number of cutting surfaces, the cutter diameter. The helix angle reduces the load on Like CAT Tooling, BT Tooling comes in a range of sizes and uses the same NMTB body taper.
same main components that enable the workpiece to be Hence the idle time spent in positioning and retracting the tool is avoided. A mill drill also has a large quill that is generally locked during milling operations and released to facilitate drilling functions.
cutting the workpieces from the stock also contributes In this approach, the tool movement is unidirectional.
Sufficient R&D spending probably would not have happened within the machine tool industry alone; but it was for the latter applications that the will and ability to spend was available. NC/CNC machining centers evolved from milling machines, which is why the terminology evolved gradually with considerable overlap that still persists. There are two subcategories of vertical mills: the bed mill and the turret mill. Most of the machines that Bridgeport made between 1938 and 1965 used a Morse taper #2, and from about 1965 onward most used an R8 taper. of operations may be performed to the workpiece to yield various operations to be performed and the amount of In 1920 the new tracer design of J.C. Shaw was applied to Keller tracer milling machines for die sinking via the three dimensional copying of a template. form, they also differ based upon their orientation, There is no pull stud with this type of tooling. However, secondary processes may be used to improve the The older a machine, the greater the plurality of standards that may apply (e.g., Morse, Jarno, Brown & Sharpe, Van Norman, and other less common builder-specific tapers). called G-codes or NC-codes.
arranged in a helix. materials for which it is best suited. operator adjusts the position of the cutter by using